A new solution to integrate electric vehicle charging into the urban scape

Significant Electric Vehicle (EV) adoption is crucial for the UK to meet its climate targets and tackle air pollution in cities. In its 2018 transport roadmap, the ‘Road to Zero Strategy’, the government has set out a target of 50-70% ultra-low emission vehicles sales by 2030. Quite a jump compared to today’s sales, which are still under 5%, but achievable as exemplified by Norway where EVs now make up about 50% of car sales.
The role of charging infrastructure
While battery costs and consumer acceptance of EVs are improving, there are still some barriers to uptake. In the short term, there is a supply issue – demand is currently outstripping the volume manufacturers can produce. This is not however a long-term issue, with virtually all major manufacturers ramping up their investment in production. The more worrying barrier that will inhibit rapid uptake of EVs, after the production shortfall hiatus, is a lack of public recharging infrastructure.
Do EV drivers need public infrastructure anyway? If they can charge at home at night, the answer is yes but not much – it will of course depend on how often they do long distance trips. Based on UK travel statistics, charging at home should cover about 75-90% of charging needs. Statistical conclusions regarding real needs won’t change drivers’ appetite for more public charging infrastructure though. This issue has been highlighted recently by the public through an AA survey which found that 80% of non-EV drivers are concerned about the lack of public chargepoints.
And what about drivers who won’t be able to charge at home at night? A substantial 8 million vehicle owners in the UK today do not have access to a garage or driveway. They simply cannot access the practical and low-cost home charging option. For them, access to public infrastructure is an absolute necessity. While 8 million might not seem much compared to a national car fleet of about 30 million, these are typically in urban areas, where air quality issues are the worst. If they are the last ones to convert to EVs (whether the cars are private or shared), urban dwellers will miss out on air quality improvements.
How to charge an EV parked on-street
What solutions are there for the widespread and cost-effective installation of on-street charging infrastructure?
Several technologies are emerging – each with advantages and drawbacks:
Standalone on-street charge point – these are often inconveniently located (i.e. not targeted at residents), expensive, and the bulky equipment presents access issues on the pavement e.g. for wheelchair usersLamppost charging – cheap and quick to install but limited to lampposts close to the road (otherwise cables have to cross pavements, be fed underneath with a satellite bollard, or slotted into trenches). Their power is typically restricted to 2-5kWWire trenches – gives the user access to a home electricity tariff, by slotting a cable in the pavement between a home charge point and a car. This needs the car parked directly outside the house, which can’t be guaranteedPop-up charging – no clutter when the charger is hidden in the pavement but requires extensive and expensive street works as technology is installed underground, and moving parts raise reliability and maintenance concernsRapid charge hubs – no evidence yet that this is a solution for residents, although research is on-going with Innovate UK funding.The drawbacks identified above prevent the widespread installation of any of the charge point technologies, therefore there is still a gap in the market for new charge point types to meet charging needs. One such technology could be the one being developed by Trojan Energy. Trojan Energy is an exciting new charge point company, set up by a budding group of oil engineers, who are keen to utilise their skills in the low carbon sector. They have designed an innovative solution to on-street charging, which enables the deployment of charge points at scale, covering entire streets at relatively low cost.
The Trojan Energy system – a flush charge point
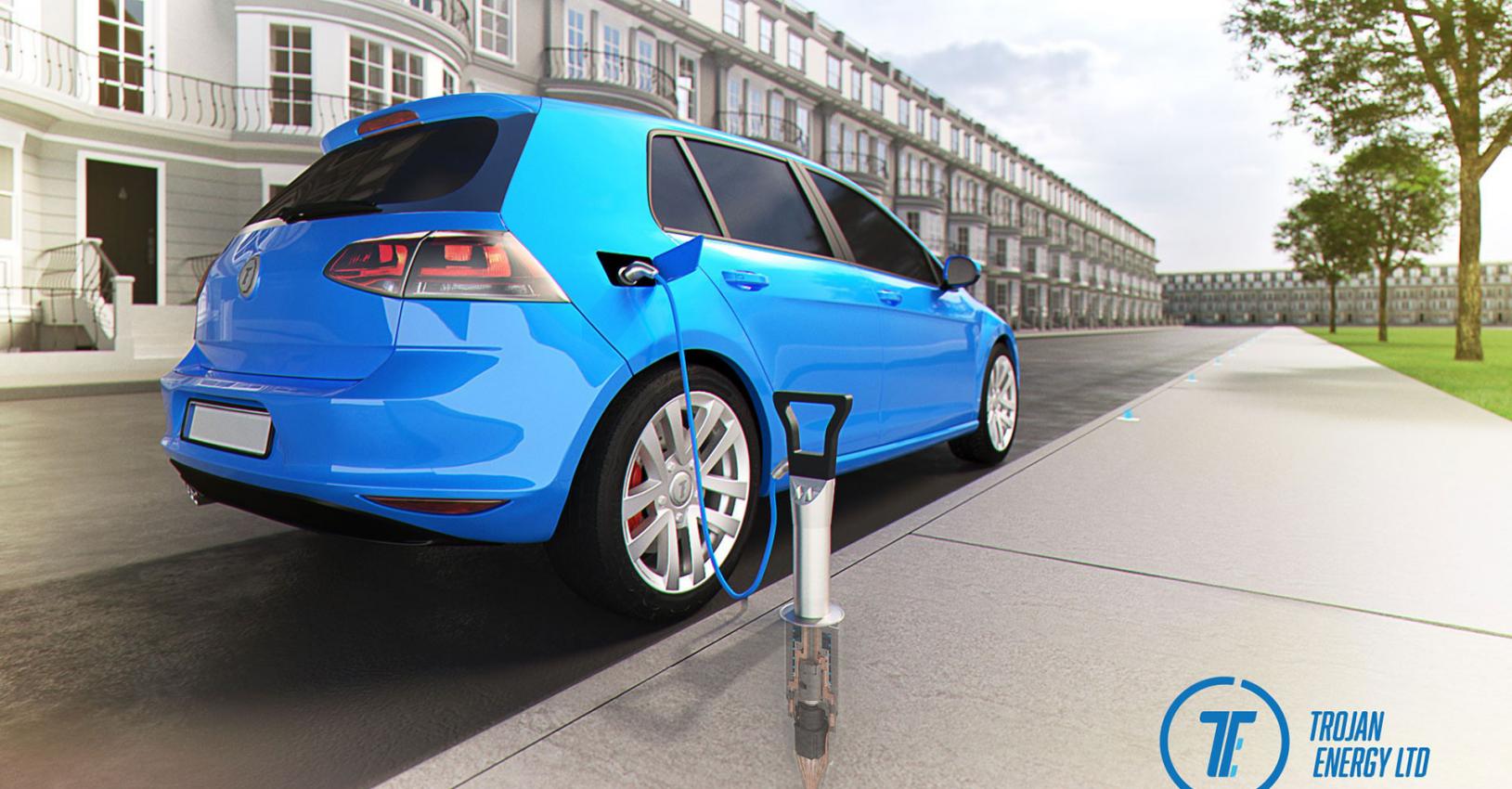
The main features of the Trojan Energy system include a flush charge point connector that is level with the pavement and a ‘lance’ which is used to connect the charge point to the vehicle. Connectors are placed approximately 5m apart, allowing EV owners to conveniently charge when parked at any point along the street. This reduces tension between residents, as no parking bays would be ring fenced for EVs.
An advantage of the Trojan technology is that there is no permanent footprint on the edge of the pavement. Only when the car is charging is there an obstacle; this maintains the safety of the pavement and access requirements. Another novel aspect is that up to 20 cars can be charged simultaneously, from the same grid connection, through the Trojan box. The obvious upside is the saving on connection costs. This aggregation of cars also presents exciting opportunities for network operators: having multiple cars to a point makes the load on the point larger as well as more predictable. This is interesting because actively adjusting the power demand from EVs will become essential once EVs are ubiquitous – the electricity grid would not be able to cope with drivers’ tendency to all plug-in at the end of the day. Cutting 5kW from a car charging at 7kW could be very inconvenient for a driver, whereas spreading a 5kW curtailment over 10+ cars will go unnoticed.
The list of advantages continues: the connectors feed from the 3-phase cables present along street pavement, allowing rates from 3 to 22kW per charger. The high rates would be of interest to drivers of EVs with large battery packs, or shared vehicles which have shorter dwell times. The biggest advantage is the scale of deployment – a whole street could be converted. In fact, this solution is designed for mass rollout.
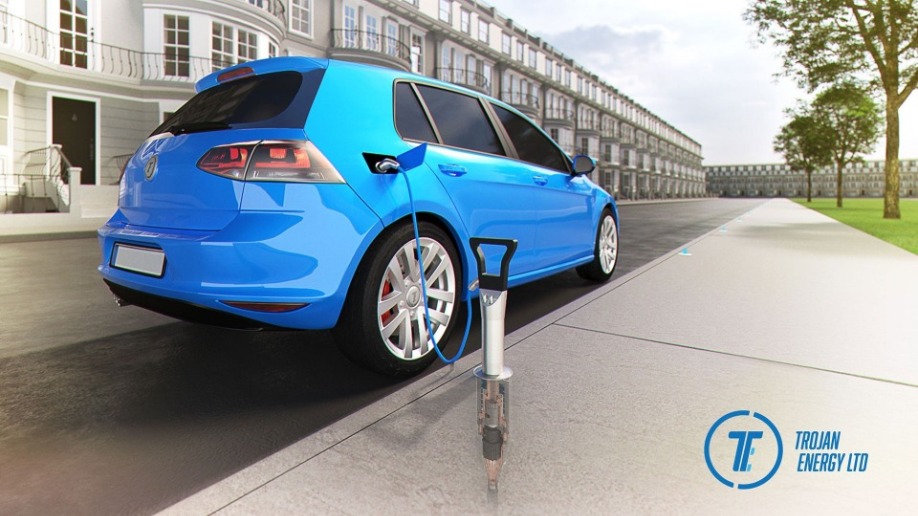

Figure 1 The Trojan Energy charge point and lance - a neat solution to on-street charging, with street clutter only at the pavement edge when the vehicle is charging

Figure 2 The full Trojan Energy System - with one grid connection every 20 charge points, saving on connection costs
Research findings and next steps to deployment
The Trojan Energy solution has recently been investigated in a Feasibility Study entitled STEP – Subsurface Technology for Electric Pathways – which is part of the Electric vehicle charging for public spaces: feasibility studies competition, funded by the Office for Low Emission Vehicles (OLEV) in partnership with Innovate UK (IUK). In this study, led by Element Energy, Trojan Energy worked alongside the London Borough of Brent, Birmingham City Council and UK Power Networks to validate several aspects of the technology.
The Feasibility Study mainly involved the testing of the system to ensure compatibility with the grid, identifying potential sites for a trial in Birmingham and Brent, and gathering feedback on the technology. The results were positive all around: the prototype passed all the technical tests with flying colours, several streets have emerged as good candidates for the tech and feedback has been very positive.
Feedback was collected from councillors as well as EV and would be EV drivers. 65% of consumers surveyed said they would be willing to have the Trojan Energy solution installed outside their house (a high portion of those unwilling are those who wouldn’t consider purchasing an EV in the first place). In the workshop with Brent EV owning residents, 87% wanted to sign up to have the sleek connector in their street.
The next stage of the IUK project is a Demonstrator Trial of the technology, later this year. Trojan Energy plan on installing several hundred connectors in London and Birmingham to demonstrate that the real-world fully operational system provides a seamless and convenient solution to on-street charging. This trial is conditional on receiving funding from IUK in the next round of bidding, which ends at the beginning of May.
If successful, Trojan Energy will take the first step to providing a solution for the biggest problem facing EVs in the future, paving the way for a world in which EVs are truly ubiquitous.
Authors: Sarah Clements, Consultant and Celine Cluzel, Director, from Element Energy
Element Energy is a strategic energy consultancy, specialising in the intelligent analysis of low carbon energy. We provide consultancy services across a wide range of sectors (smart electricity and gas networks, energy storage, carbon capture, renewable energy systems and low carbon vehicles). Our work involves consulting on both technical and strategic issues – we believe our technical and engineering understanding of the real-world challenges support the strategic work and vice versa.
http://www.element-energy.co.uk/
Celine Cluzel will be speaking at TaaS Technology Conference, 10th July 2019, Birmingham, UK.
A new solution to integrate electric vehicle charging into the urban scape
Modified on Tuesday 23rd April 2019
Find all articles related to:
A new solution to integrate electric vehicle charging into the urban scape


 Add to my Reading List
Add to my Reading List Remove from my Reading List
Remove from my Reading List